Dr. Cavalli’s team will combine single-cell approaches and epigenomic approaches in mouse and human sensory neurons to understand the neuronal and non-neuronal mechanisms orchestrating nerve repair.
Valeria Cavalli receives an R35 award from the NIH


Dr. Cavalli’s team will combine single-cell approaches and epigenomic approaches in mouse and human sensory neurons to understand the neuronal and non-neuronal mechanisms orchestrating nerve repair.
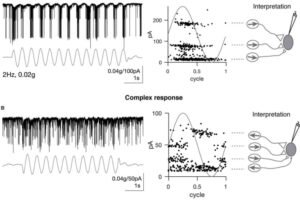
The Bagnall lab finds the complexity of tuning in a vestibular neuron arises from the diversity of inputs it receives, and that this complexity can be predicted from these inputs.

A study from Adam Kepecs’s lab in mice and people offers a new approach to investigating mental illnesses.
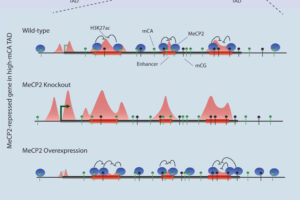
In a new study, the Gabel lab explores the role of MeCP2 in regulating enhancers.
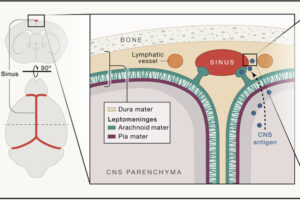
The Kipnis group describes a mechanism by which patrolling immune cells from the peripheral immune system survey cues about the immune status of the brain that accumulate in the cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the brain.

The Padoa-Schioppa lab demonstrates that choices are based on the computation of values of each option.