A new study from the Goodhill Lab finds the genetic variant underlying an autism disorder causes changes in fish’s social behavior, preference in visual environment, and neural activity.
Zebrafish advance as a model organism for Fragile X Syndrome
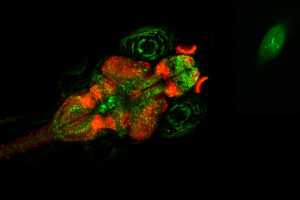

A new study from the Goodhill Lab finds the genetic variant underlying an autism disorder causes changes in fish’s social behavior, preference in visual environment, and neural activity.
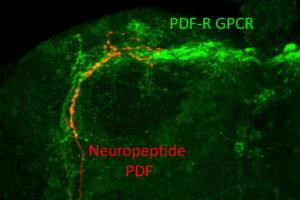
Phosphorylation of a receptor controls how messages from the neuropeptide PDF—which influence dawn and dusk activities in Drosophila—are curtailed on a daily basis to adapt the circadian clock to changing daylight.
A study of individuals with congenital corpus callosum dysgenesis suggests they face social difficulties due to being more easily influenced and less aware of being tricked.
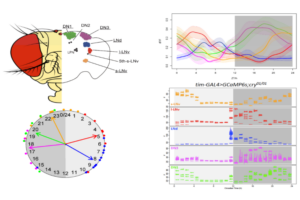
The slow and fast rhythms reflect distinct cellular processes yet nevertheless have a co-phasic relationship.
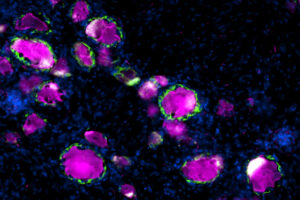
SGCs have been the subject of intense scrutiny for their involvement in inflammation, pain and nerve injury. The results confirm that rodents are a reliable model for translational research on these cells.
Finding therapies for fragile X may depend on understanding the many ways the protein’s loss affects the brain.

Camillo Padoa-Schioppa, PhD, has developed a manual of tools for analysis of economic choices.
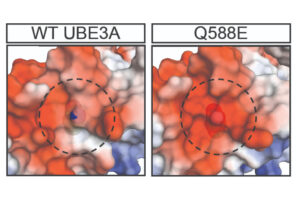
Assistant Professor Jason Yi’s group applied the technique to variants of unknown significance in UBE3A, the gene that underlies Angelman syndrome.
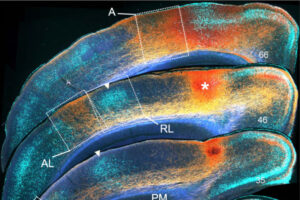
The Burkhalter lab finds that areas are embedded within a hierarchical network in which image fragments from the retina are sent through bottom-up pathways to extract percepts, and top-down pathways from higher to lower areas provide prior knowledge for interpreting the visual scene.

Paul Shaw’s lab demonstrates that sleep induction in fruit flies otherwise unable to perform learning and memory tasks rescues their behavioral performance.