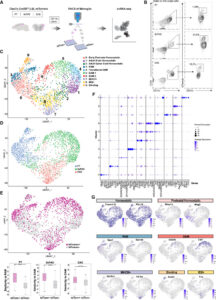
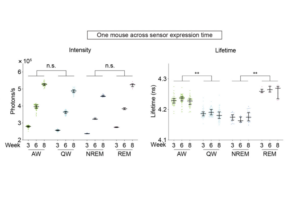
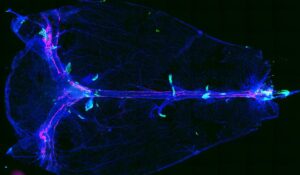
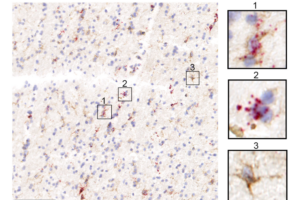
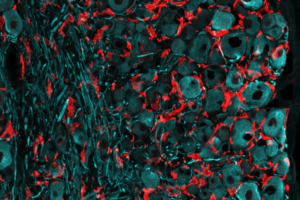
A recent study published in Immunity by the Li lab opens a new chapter for the study of microglial function in development and neurodegeneration with remarkable precision.
Li Lab study published in Immunity further explores microglial states (Links to an external site)